IFRS Guidance for Allocating Purchase Price in Education
IFRS Guidance for Allocating Purchase Price in Education
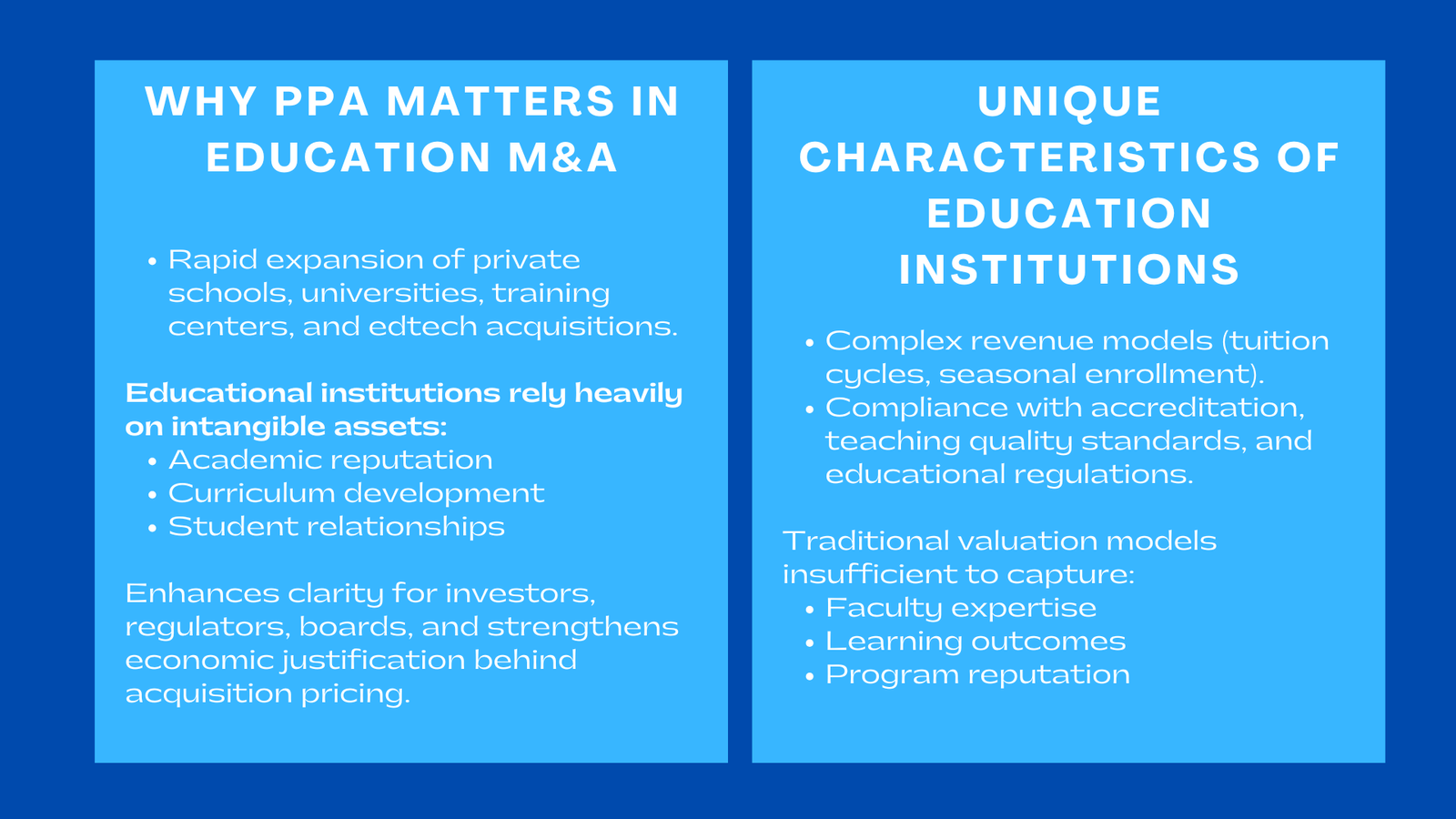
The purchase price allocation as developed in the education sector has gained relevance following the massive growth of mergers and acquisitions by the private schools, universities, training centers and learning institutions that are edtech based. In contrast to commercial enterprises where success is largely pegged on tangible assets or on classical sources of revenue, education institutions obtain a significant economic worth in terms of abstract characteristics like academic reputation, curriculum development, student relationship, program quality, accreditation and local trust. The process of purchasing an educational entity is a sensitive procedure under the reporting of the IFRS standards, and thus, when the respective institution is sold to someone, the allocation of the purchase figure will be done with enough attention to value the assets, liabilities, and other unrecorded elements of an institution. Such an organised allocation is not only in the interest of increasing the transparency of the financial decision-making but also aids investors, regulators, and boards to discern the actual economic motivation behind the value of education to the economy.
Due to the dynamic nature of the global education sector, learning facilities, vocational schools, and tertiary institutions are being bought by institutional investors and individuals in large numbers. There is a need to allocate the purchase price under the IFRS carefully on these transactions since education institutions have rare and mission driven qualities that education institutions lack, education institution purchase price allocation just as in case of normal profit-making business models. The IFRS M&A reporting provides that financial statements of the acquired institution are presented in reality and hence have a clear understanding of the factors that lead to sustainable growth, stability in student enrollment, and scalability of programs. Purchase price allocation (PPA) has become a crucial element of the acquisition of an enterprise in the education sector due to the ever-increasing emphasis on transparency, accountability, and compliance.
The Increasing Significance of IFRS-Compliant Reporting in Education M&A
Connecting Academic Value and Financial Reporting Through PPA
In educational settings, the environment under which the institutions exist is based on academic quality, the long-term relationships with students, curriculum relevance, and accreditation as factors that bring about the value of the institutions. Nevertheless, these factors do not necessarily mirror into the traditional financial reports. Purchase price allocation fills this gap with allocation and valuation of intangible elements that serve as great contributors to economic results. PPA that is based on IFRS standards facilitates an acquirer to measure non-physical qualities including brand integrity, alumni faith, student interaction, and dissimilarity in the program. Through the association between scholarly assets and financial outcomes, the PPA procedure—often supported by purchase price allocation advisory Singapore firms—maintains the provision of a wholesome picture to the stakeholders in terms of the operational health and strategic opportunities of the institution.
Supporting Informed Decision-Making in Education M&A
Having a better implemented PPA will enable investors and education groups to recognize the economic sense of the acquisition price. The nature of educational institutions tend to have an increased stability in terms of revenues due to the multi-year planning of the reasons that lead to enrollment of students, student loyalty, and close ties to the industry. These attributes require careful consideration to help in establishing whether the acquisition price can be realized in terms of its long-term value. The PPA process enables analysts to evaluate the capability of the institution to experience a rise in the number of enrolments, academic quality, and brand name. This clarity of strategy helps in negotiation, builds the confidence of investors and helps in planning the post-acquisition integration.
Navigating IFRS Complexity in Education-Sector Transactions
Unique Financial and Operational Structures in Education
The complexity of the structures of the education institutions into which they exist is vastly different, as opposed to commercial industries. Multiple program services, fluctuating academic schedules, seasonal student attendance flats, and revenue models based on tuition should be analyzed in more detail under IFRS. Also, the institutions need to adhere to accreditation standards, educational standards as well as the quality assurance standards, which affect the financial sustainability and the profile of operational risks. These attributes demand that the analysts do not consider the performance merely in terms of the financial information, but in terms of academic and institutional factors that determine the long-term sustainability.
Why Traditional Business Valuation Approaches Are Insufficient
The current business evaluation practices are not able to fully reflect on the multidimensional worth of educational institutions. Such variables are student satisfaction, learning outcomes, expertise of the faculty, institutional accreditation, and program reputation that will play a major role in long-term performance but do not necessarily be reflected in financial statements. According to the IFRS, the intangible assets have to be assessed in terms of identification, separability, and quantifiable economic advantage. Traditional models will thus have to undergo changes to include academic measures, reputation of the institutions and stability of the enrolling process.
Identification and Valuation of Educational Intangible Assets
Assessing Academic Reputation and Institutional Brand
The good name of a learning institution is usually one of the most valuable intangible resources of the institution. The student enrollment decisions and power of tuition price is determined by the academic prestige, community trust, alumni engagement, and recognition of the brand. Under the IFRS, such intangible investments can only be regarded under certain criteria thus careful consideration of their economic effect should be taken. Researchers have to find ways in which branding the institution leads to a long term enrollment growth and whether advantages based on reputation can be translated into financial benefits which can be measured.
Valuing Student Relationships and Enrollment Stability
Student relations are a key source of future revenue, especially where the enrolment system is made in multi year academic courses. Cohort stability of students, retention, and re-enrollment and the parental trust are a major influencer on the value of institutions. Purchase price allocation is a procedure that should be carefully analyzed regarding these aspects, and the predictability of such a cash flow and its safety need to be evaluated. The relationships should be valued under the IFRS rules, and only quantifiable economical proceeds should be identified.
Assessing Curriculum Assets, Accreditation, and Program Quality
Another important intangible asset is the curriculum of a school or university; like its framework, intellectual composition and pedagogical materials. When combined with approved training programs, training modules specialization, and in-house learning techniques, they can be competitive differentiators. The aspects are valued according to their capabilities to bring out future benefits under the IFRS model, which may be increased enrolment, increased tuition fees, or the potential of increased markets. In specific, accreditation helps to strengthen the institutional credibility and affect the financial sustainability, thus becoming an essential component of asset valuation.
IFRS Treatment of Deferred Revenue and Student Prepayments
Reassessing Tuition Prepayments and Enrollment Fees Under IFRS
In most cases, education facilities get tuition payments in advance which accumulate to large levels of deferred revenue balances. In the case of IFRS, the deferred revenue should be realized in accordance with the cost of the remaining performance obligations and not only the amount that the invoice represents. This necessity is demanded to assure that the financial reports are appropriate to indicate the actual economic cost of rendering future academic provisions. To establish the deferred revenue at fair value after acquisition, analysts are required to evaluate the program length, delivery programs and outstanding instructional obligations.
Impact on Post-Acquisition Earnings and Financial Stability
The reassessment of the deferred revenue that is caused by the IFRS affects the recognition that will be achieved in the subsequent reporting periods. The ones that are subject to large advance payments need to expect a change in earning patterns since these changes change the recognition of earnings. Reporting after the acquisition should bring the cost of servicing the education services that will have to be undertaken continuously, and it needs to be monitored and complied with to ensure that the financial records are accurate and that it retains the trust of the people who have invested their money into it.
Interpreting Goodwill and Long-Term Educational Value
Understanding Non-Separable Institutional Advantages
Goodwill is another term used to denote the premium that an acquirer is ready to pay in circumstances that are not identifiable, but are likely to be strategically important to the educational institution. These can be institutional culture, quality of teaching, trust of their community, loyalty of the alumni, and synergistic advantage of merging the acquired institution with a bigger learning system. Goodwill describes the overall value of the institution, which cannot be described with reference to individual assets but adds much value to the long-term financial outcomes.
Monitoring Goodwill Through Academic and Market Performance
The IFRS mandates that the goodwill should be impaired on an annual basis and thus it is highly necessary that the education institutions regularly test their performance indicators on the basis of enrollments, student satisfaction, success of the programs and its relevance in the market. These pointers are used to reveal the sustainability of the economic expectations in goodwill. Measuring makes sure there is a fit between strategic workings and realities.
Applying PPA Across Different Types of Education Transactions
M&A in Private Schools, Colleges, and Training Centers
PPA assists in the assessments of different education providers, including the K-12 private schools as well as vocational schools and colleges. The types are unique in terms of the intangible attributes, i.e., the teacher-based expertise, program accreditation, cooperation with industries, and diversity of students. With thorough allocation, shareholders can have a perception of the economic value of each model as well as the aspects that conform to the long-run strategic objectives.
Edtech Acquisitions and Digital Learning Platforms
The edge of proprietary software and user information, content libraries and technology-driven delivery models further complicate the task of digital-learning platforms and edtech companies. In this case, PPA should use software valuation, digital content evaluation and user interactivity measurements. These elements play a major role in determining the future revenue and scalability and IFRS provides that the elements are assessed technically and financially with accuracy.
Handling Valuation Uncertainty in Newly Established Institutions
New and fast-growing institutions can have little historical data; thus, it is hard to value. The evaluations of long-term viability usually involve the use of scenario-based modeling, projection of enrollments, and the ratings of regulatory compliance by analysts. These uncertainties are organised through PPA structures, which enable the investors to get the risk profile of the institution and the growth potential of the institution as real.
Strengthening Strategic and Analytical Thinking in Education M&A
Developing a Forward-Looking Approach to Academic and Financial Growth
Purchase price allocation is also an incentive that allows investors and financial practitioners to take a strategic and futuristic approach in appraising schools. This entails the study of the demographic trends, changing preference of students, adoption of technologies in the learning facilities as well as changes in regulation that define the future enrollment and financial prospects. This will help in making sure that the conclusions of PPA will refer to the past performance as well as the changing of the position of the institution in the market.
Enhancing Analytical Discipline Through Institutional Performance Metrics
The analysts should combine financial data with academic performance data like retention rates, graduation rates and competitiveness of the program. This multidisciplinary test enhances the analytical rigor needed in the PPA that needs to be reported in accordance with the IFRS, and gives a comprehensive picture of the institutional value.
Communicating PPA Outcomes to Education-Sector Stakeholders
Translating Complex IFRS Valuation Into Practical Institutional Insight
Communication plays an important role in ensuring that educational boards, leaders of the faculty, regulators, and investors, know the outcomes of the PPA process. There are a lot of stakeholders who might be unaware of IFRS M & A reporting requirements and, therefore, the clarity and coherent explanation in the form of transparency is necessary. Effective communication improves the level of trust and makes financial reporting consistent with the mission and strategic direction of the institution.
Ensuring Transparency in Governance and Audit Readiness
An effective PPA also provides good governance procedures being well documented making audit reviewing easy. Open disclosure of assumptions, methods of valuation, and reporting implication enhance confidence of the stakeholders and helps in the adherence of the regulation systems in the education sector.
Integrating Technology and Analytical Tools in Education PPA
Leveraging Enrollment Analytics and Academic Data Systems
Contemporary schools and universities are using digital systems to oversee enrolment, student performance, school academic program and learning results. The incorporation of these datasets into PPA will be able to offer a greater depth of understanding concerning the stability of the cash flow, the recurring of the enrollment cycles, and demand of the programs. Valuation models are also more factual and realistic of the institutional realities by integrating real-time educational analytics into them.
Using Advanced Modeling Tools for IFRS Reporting
The use of analytical software and automation tools as well as dynamic forecasting models increase purchase price allocation reliability. Such tools allow the analysts to handle huge amounts of data as well as simulate the enrollments and model the tuition revenue in various scenarios. These abilities can bring the results of PPA to the level of the challenging contemporary educational setting.
Institutional Advantages of Rigorous Purchase Price Allocation
Supporting Financial Transparency and Responsible Governance
A comprehensive PPA system offers a clear picture of the economic situation of the institution since the financial statements give a true picture of the situation. The transparency enhances leadership within practicing governance, boosting accountability, and making effective decisions within the leadership teams.
Building a Culture of Analytical Excellence in Education Management
The regular use of PPA will ensure that there is a culture of analytical rigor in educational institutions. The culture promotes evidence-based decision-making, financial planning, and long-term institutional resiliency by aligning financial insights and achieving academic goals.
Conclusion to IFRS Guidance for Allocating Purchase Price in Education
With the transformational expansion of the education sector through innovation, globalization and integration of technologies, purchase price allocation has become a very vital instrument towards maintaining financial transparency and alignment of strategic direction in the education sector IFRS M&A reporting activities. Having evolved the academic value, institutional relations and operational power into the orderly financial indicators, IFRS-conformable PPA optimizes transparency, fortifies investor confidence and promotes the move toward sustainable development of education. All experts in the field, and in particular acquirers, institutional heads, and financial managers, the principles of education institution purchase price allocation is of great importance in trying to survive in what is becoming a more intricate and dynamic educational environment.