Professional Tax Implications IFRS Certification
Tax Implications of Purchase Price Allocation and Consideration Adjustments
Learn Professional Tax Implications IFRS Certification
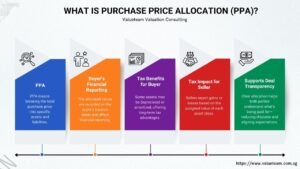
Purchase Price Allocation (PPA) of M&A transactions is not only the basis of accounting goodwill but also tax consequences are serious. Consideration alternatives, including contingent or deferred payments, have an impact on deductibility of expenses, recognition of deferred tax and the net effective tax rates. These implications are essential to the corporate finance staff, tax advisors as well as CFOs in deal structuring.
In addition to compliance and reporting, proper knowledge about PPA and considerations of corrections allows businesses to ensure charge with post acquisition cash flows, and decrease tax risks, which could appear. Through the proper planning of the purchase price allocation and its effect on the taxable income, the companies can make the informed decisions that can contribute to financial efficiency of the company, retain the shareholder value, and collectively to the long-term corporate strategies, as well as such allocation will ensure the seamless acquisition integration of the new business.
By accurately mapping the interplay between PPA and taxation, organizations can anticipate the impact of amortization on taxable income, plan deferred tax recognition appropriately, and create smoother post-acquisition integrations with minimal disruption to operational cash flows.
What IFRS Certification Covers and Its Global Recognition
The IFRS Certification is an internationally accredited certification that aims at providing the profession in finance and accounting with a detailed knowledge of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) – the common business accounting language. It has detailed training on interpretation, application, and reporting of financial transactions as required by the international accounting principles of the international accounting standards board (IASB).
The certification is comprehensive and embraces most of the topics in the IFRS, such as the conceptual framework of financial reporting, financial statement presentation, revenue recognition (IFRS 15), leases (IFRS 16), financial instruments (IFRS 9), and business combinations (IFRS 3). The participants also benefit by learning about IAS 12 (Income Taxes), IAS 36 (Impairment of Assets), and IAS 37 (Provisions and Contingent Liabilities) that are very important to any other professional in matters that relate to tax and financial reporting implications.
In addition to the technical coverage, IFRS Certification programs tend to focus on real world applications in the form of case studies, exercises and comparisons between local GAAP and IFRS. This pragmatic approach assists the professionals to comprehend the effect of IFRS on financial reporting, taxation planning and compliance.
Employers, regulatory agencies, and professional bodies are very concerned with IFRS Certification all over the world. More than 140 nations have implemented or oriented their reporting standards on IFRS and therefore certified professionals are in high demand by multinational corporations, audit firms, and financial institutions.
The certification is an indicator of international competence and credibility. It shows that a professional can make clear, similar and internationally acceptable financial statements, which is one of the most important conditions of businesses that are cross-border. Be it in accounting, tax advisory, or corporate finance, an IFRS Certification provides practitioners with international career advantage and enhances their understanding of international reporting and alignment of tax.
Key Skills and Competencies Gained Through Certification
An IFRS Certification offers a combination of technical, analytical and strategic skills that professionals require in order to succeed in the field of finance and taxation in the modern society. The program improves not only the conceptual but also the practical application that enables the participants to cope with the complex financial reporting settings.
To begin with, applicants become skilled in the process of interpreting and implementing IFRS standards. This is also involving the capability to interpret financial statements, determine important accounting problems, and maintain international standards. Some of the areas covered to professionals include revenue recognition, lease accounting, business combinations, and financial instruments all of which are directly taxable.
Analytical thinking is another important skill that is developed. The certification educates practitioners to analyze financial the effect of accounting choices, examine the effects of taxation caused by temporary and permanent differences, as well as utilize professional judgment in unclear instances. Analytical competence helps to make better decisions especially in balancing accounting treatment and tax requirement.
The participants also gain ample knowledge in deferred tax accounting as provided in the IAS 12 accounting standards and this allows them to separate the tax bases amongst financial reporting. This is particularly useful when working on corporate taxation, audit, and financial strategy where timing differences and adjustments may greatly impact on profitability and compliance.
In addition to technical skills, IFRS Certification develops working global communication and reporting. Qualified personnel is able to participate successfully in international stakeholder relations, audit and regulation, presenting information on finances that are internationally transparent.
Soft skills like attention to detail, moral judgment and strategy thinking are also reaffirmed during the program. These properties assist the professionals to change according to the new regulations, to comply with them, and to maintain the integrity in reporting practices.
Finally, the IFRS Certification makes professionals a perfect expert, able to bridge financial reporting and taxation, and increase their career and worth in the international financial arena.
Tax Treatment of Consideration Adjustments
Deferred Consideration:
When compensated economy wise, payments are normally deductible. Timing has an impact on cash tax and deferred tax accounting.
Contingent Consideration:
The deductibility is determined by the ability to regard payment as an obligation which is enforceable during acquisition. In certain jurisdictions, the deductions might be made in cases where payments are probable and quantifiable.
Equity Consideration:
Ventures that are mostly issued do not create any tax deduction, although it can influence sale of capital or loss.
Purchase Price Allocation:
The inclusion of buying price in tangible assets, identifiable intangibles and goodwill influences the depreciation, amortization and computation of deferred taxes.
Deferred tax liabilities (DTLs) and assets (DTAs) are tax implications of purchase price allocation in M&A transactions recognized to reflect the temporary differences between book and tax bases of these assets and liabilities. For instance, the fair value step-up in intangible assets may create DTLs, while contingent liabilities recognized for accounting purposes might create DTAs. Proper documentation and periodic reassessment ensure that deferred taxes are accurately reflected and that financial statements remain compliant and audit-ready.
Strategic Considerations
Tax-sensitive PPA and consideration campaigns can maximize post acquisition cash flow, minimize tax risk and increase trade economics. There is intimate cooperation between the accounting, tax and deal advisory teams so as to harmonize the valuation, reporting and tax goals.
Well implemented, a tax-sensitive purchase price allocation model enables organizations to planfully find value to assets in a fashion that would maximize the tax benefits of depreciation and amortization without compromising on the IFRS-compliant PPA and deferred tax treatment for acquisitions and the national tax laws. This method does not only increase the quality of financial reporting but also offers practical savings that increase the returns of deals in general. The process of tax planning into PPA assists companies to determine timing disparities, predict the existence of deferrals and arrange future payment like earn-outs or deferred consideration in a manner that promotes after-tax cash flows maximally.
Furthermore, it is recommended to keep clear records of tax assumptions, procedures and computations as part of augmenting the audit preparedness and adherence to regulatory regulation. It gives the investors and stakeholders also some confidence that the acquisition was not done with financial prudence but in the long run. In the long run, tax-efficient PPA policies lead to an enhanced level of capital management, financial transparency, and post-acquisition performance, which is more robust, matching the importance of tax efficiency with corporate value creation and strategic growth.
Conclusion
The accounting, financial and strategic planning of M&A are interconnected and in the case of projecting the accounting, finance and strategic planning PPA and consideration adjustments, the way the allocation is structured and documented is vital to make sure that compliance is met, risk averted and financial performance maximized. In the case of businesses that deal with intricate transactions, it is important to incorporate tax insights into the valuation and consideration planning in an endeavor to extract the entire value of the acquisition.
Besides the benefits of compliance, knowledge of such tax implications will help organizations maximize the efficiency of cash flow and reduce surprises after the acquisition. The coordination of the purchase price allocation strategies with the tax planning would help companies to have informed investment decisions, to place better deals and to have a strong overall financial position and, finally, by strategic objectives.